metalr-likelihood ratio meta-analysis r packageTraditional 95% confidence intervals (CIs) in updatad meta-analyses do not usually result in the expected 95% coverage because earlier meta-analyses often fail to exclude the null. Thus, a likelihood ratio based method that is independent of type 1 error as proposed by Dormuth et al, 2016 could be used to obtain adjusted confidence intervals that are more intune with reality. These “intrinsic” confidence intervals (ICIs) are wider than the traditional confidence intervals.
It turns out that traditional 95% CIs are 1/7th as likely as their corresponding confidence intervals; this is contrary to the natural tendency of interpreting null hypothesis as being 5% or 1/20th as likely as the MLE. In order to correct this disconnect, the likelihood ratio meta analytic (LRMA) method, independent of p-values or sample size, is used.
The method is implemented for estimating rate ratios or odds ratios in epidemiological studies. For example, suppose we consider the natural logarithm of rate ratio (log(RR)) then the likelihood ratio (LR) comparing the RR under the null hypothesis (μ0 = RRH0 = 1.00) vs some alternative hypothesis (μ1 = RRHA) is given by
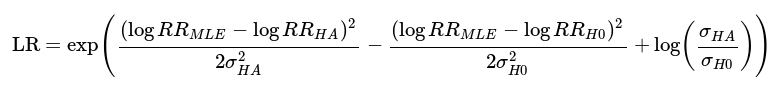
where log() denotes the natural logarithm scale and σ2 corresponds to the variance of RR under the null and alternative hypothesis. See Dormuth et al., 2016 for more detailed explanation of the method.
R software package to estimate traditional 95% CIs and 95% intrinsic CIs of effect estimates (rate ratio and odds ratio) in epidemiological studies. The package includes the following functions
The ici.rr() Function: estimates 95% intrinsic confidence interval for rate ratio.
The ici.or() Function: estimates 95% intrinsic confidence interval for odds ratio.
The metalr_or() Function: estimates total effect estimates (MLE of combined odds ratio), the 95% CI and 95% intrinsic CI in fixed effect and random effect meta-analysis. Individual study effect estimates and their corresponding CIs are also estimated.
The metalr_rr() Function: estimates total effect estimates (MLE of combined rate ratio), the 95% CI and 95% intrinsic CI in fixed effect and random effect meta-analysis. Individual level study effect estimates and their corresponding CIs are also estimated.
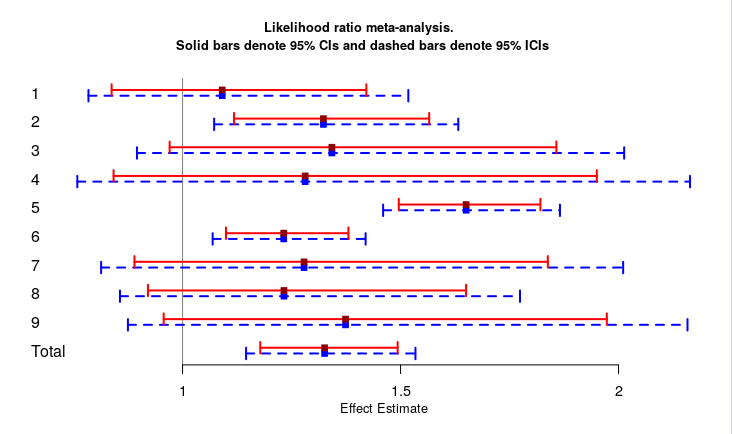
The forest_metalr() Function: returns a forest plot of the likelihood ratio meta-analysis results. The plot compares the 95% tranditional CIs and 95% Intrinsic CIs the effect estimates in a meta-analysis.
The development version of the metalr Package can be installed on GitHub using:
if (!require("devtools")){
install.packages("devtools")}
#> Loading required package: devtools
devtools::install_github("laminjuwara/metalr")
#> Skipping install of 'metalr' from a github remote, the SHA1 (5249ac96) has not changed since last install.
#> Use `force = TRUE` to force installation
We consider the randomized control trial (RCT) of clopidogrel vs Aspirin in patients at risk of ischaemic events designed to assess the relative efficacy of clopidogrel (75mg once daily) to that of aspirin (325mg once daily) in reducing the risk of ischemic stroke, MI or vascular death [1].
The study population includes a total of 9599 clopidogrel and 9586 aspirin patients were followed for 1 to 3 years (mean follow-up = 1.91 years), 939 primary outcome events in clopidogrel patients who were followed for a total of 17,636 person-years and 1021 events in aspirin patients followed for a total of 17,519 person-years. The data is compiled below.
# Clopidogrel vs Aspirin trial dataset
cases<-c(939,1021)
person_yrs<-c(17636,17519)
patients<-c(9599,9586)
The ici.rr() function calculates rate ratios and corresponding 95% intrinsic confidence intervals in epidemiological studies. The functions provides both the traditional confidence interval and intrinsic confidence limits. This allows us to compare the two confidence limits. For example, using the dataset from caprie trial, we obtain
library(metalr)
ici.rr(cases = cases,patients = patients,person_yrs = person_yrs)
#> RR ll.ci ul.ci ll.ici ul.ici
#> 1 0.914 0.8372322 0.9976566 0.8192534 1.01955
The MLE of the rate ratio is 0.914, the 95% confidence limit is (0.837,0.998) and the 95% intrinsic confidence limit is (0.819,1.020).
The metalr_rr() estimates total meta-analytic rate ratios and corresponding rate ratio. It allows fixed effect or random effect meta-analysis and outputs the 95% traditional confidence limits, intrinsic confidence limits and MLE of the effect estimate. Further, it gives estimates a measure of heterogeneity between studies in random effect meta-analysis (i.e. τ2 and the I2 statistics).
We use the toy data example provided along with the package (sample_metarr_data). That is
library(metalr)
data("sample_metarr_data")
head(sample_metarr_data)
#> C1 C2 PY1 PY2 N1 N2
#> 1 939 1021 17636 17519 9599 9586
#> 2 1099 933 19444 9999 9044 7844
In order to determine the total rate ratio effect in the above toy example, we have
metalr_rr(sample_metarr_data,refval=0,num_iter=3000,increm=0.001,method="random")
#> Warning in metalr_rr(sample_metarr_data, refval = 0, num_iter = 3000,
#> increm = 0.001, : The number of columns is greater than 4. Only columns 1-4
#> of the imputed dataset are used.
#> $Total_RE
#> limit CI ICI
#> 1 MLE 0.7437874 0.7437874
#> 2 L95% 0.4950978 0.4497785
#> 3 U95% 1.1173949 1.2299826
#>
#> $TauSq
#> [1] 0.08241624
#>
#> $Isq
#> [1] 0.9761568
#>
#> $meta_result
#> study MLE llci ulci llici ulici
#> 1 1 0.9140000 0.8372322 0.9976566 0.8192534 1.0195504
#> 2 2 0.6060000 0.5550740 0.6614333 0.5431543 0.6759486
#> 3 Total 0.7437874 0.4950978 1.1173949 0.4497785 1.2299826
The same effect estimates are obtained for individual studies and a combined total random effect estimates is also obtained. For the estimated heterogeneity index τ2 = 0.0824, we estimate the MLE of the total effect as 0.744 with the corresponding intrinsic limits (0.450,1.230).
To assess the association of higher potency statins on the risk of acute kidney injury (aki) compared to lower potency statins, a meta-analysis including 9 studies is conducted by CNODES. The dataset is presented below.
library(metalr)
data("statindata")
statindata
#> study HPcase HPcontrol LPcase LPcontrol
#> 1 AB 99 873 158 1520
#> 2 BC 285 2097 325 3164
#> 3 MB 85 680 77 827
#> 4 NS 46 371 51 527
#> 5 ON 988 7340 793 9723
#> 6 QC 602 5448 716 7983
#> 7 SK 81 526 56 465
#> 8 UK 89 755 114 1192
#> 9 US 62 509 68 767
We can used the functions ici.or() and metalr_or() in the metalr package to estimate 95% intrinsic confidence limits for odds ratio from individual studies and combined (or individual study) effect estimates from meta-analysis respectively. To demonstate applications of the functions, we have
The ici.or() function calculates odds ratio and corresponding 95% intrinsic confidence intervals in observational studies. The functions provides both the traditional confidence interval and intrinsic confidence limits. For example, the estimates obtained from QC (study 6)is presented.
ici.or(idata = statindata[6,2:5])
#> OR ll.ci ul.ci ll.ici ul.ici
#> 1 1.232005 1.09957 1.380391 1.069033 1.419821
The MLE of the odds ratio is 1.232, the 95% confidence limit is (1.099,1.380) and the 95% intrinsic confidence limit is (1.069,1.419).
The metalr_or() estimates total effects (odds ratio) from fixed or random effect meta-analysis as well as the corresponding intrinsic confidence limits. It also computes the 95% traditional confidence limits and the MLE of the effect estimate. Further, it gives estimates a measure of heterogeneity between studies in random effect meta-analysis (τ2 and I2 statistics estimates).
Below, we use the ‘statin and aki dataset’ to compute total fixed effect meta-analysis estimates.
metalr_or(statindata[,2:5],refval=0,num_iter=3000,increm=0.001,method="fixed")
#> $Total_FE
#> limit CI ICI
#> 1 MLE 1.392360 1.392360
#> 2 L95% 1.308655 1.289172
#> 3 U95% 1.479938 1.502304
#>
#> $meta_result
#> study MLE llci ulci llici ulici
#> 1 1 1.090957 0.8372716 1.421506 0.7841527 1.517799
#> 2 2 1.323121 1.1181007 1.565735 1.0724393 1.632399
#> 3 3 1.342532 0.9703811 1.857408 0.8954211 2.012900
#> 4 4 1.281222 0.8417398 1.950163 0.7585672 2.163987
#> 5 5 1.650395 1.4959698 1.820762 1.4600125 1.865604
#> 6 6 1.232005 1.0995699 1.380391 1.0690333 1.419821
#> 7 7 1.278687 0.8896541 1.837838 0.8132140 2.010590
#> 8 8 1.232578 0.9205935 1.650293 0.8564036 1.773987
#> 9 9 1.373917 0.9566770 1.973129 0.8746518 2.158169
#> 10 Total 1.392360 1.3086551 1.479938 1.2891718 1.502304
Similarly, total random effects could be estimated as shown with the metalr_or() function. We note that in both icc.or() and metalr_or() functions, the input dataframe is required to have 4 columns (not including the study name) as shown in the statin dataset above.
The forest_metalr() function plots 95% CIs and ICIs for odds ratios or ratios from a likelihood ratio meta-analysis object. Thus, we can compare traditional 95% confidence limits of individuals studies and total/combined effect estimates to their corresponding 95% intrinsic confidence limits.
Below, we use the ‘statin and aki dataset’ to plot the confidence limits obtained from the meta_or() function above
# the metalr object
library(metalr)
metalr_obj<-metalr_or(idata=statindata[,2:5],refval=0,num_iter=3000,increm=0.001,method = "random")
# forest plot of the metalr object
forest_metalr(metalr_obj)
#> GRID.VP.1::forestplot_margins